Published Date:
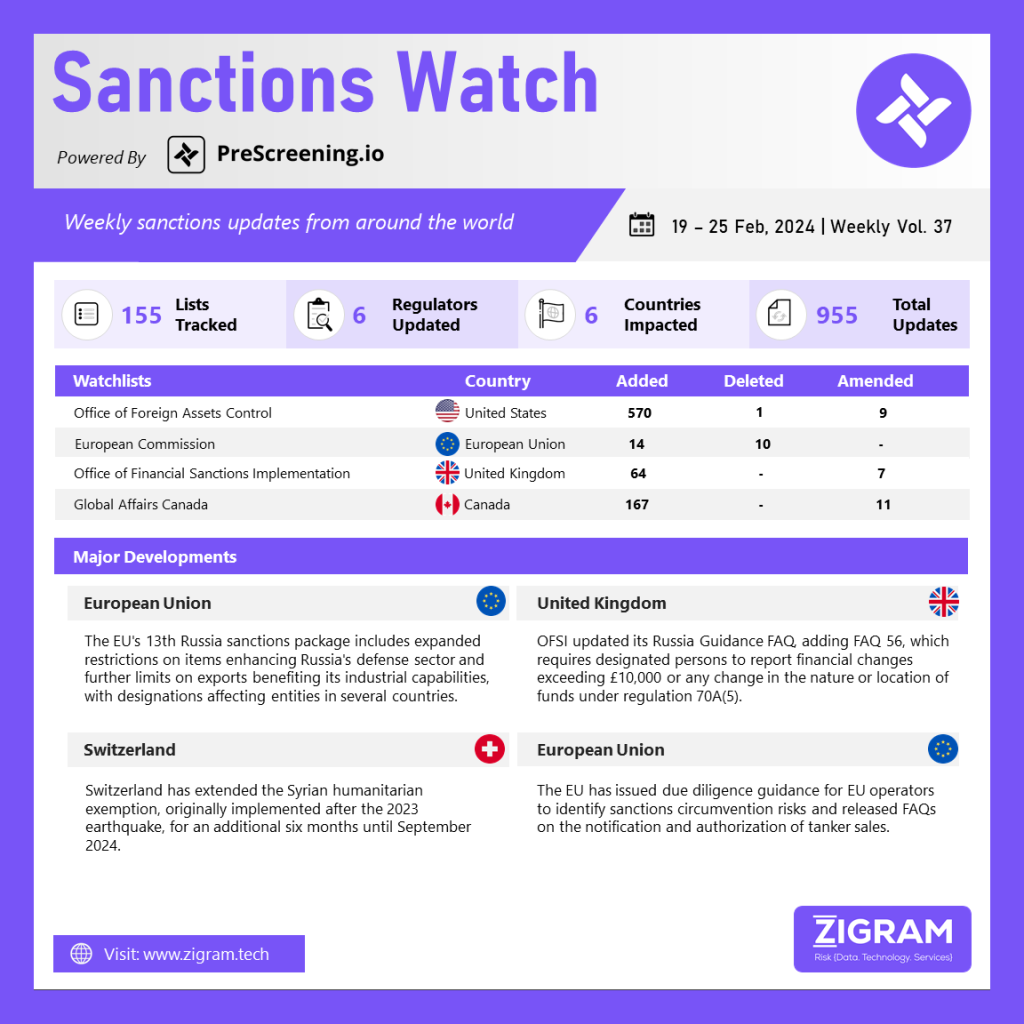
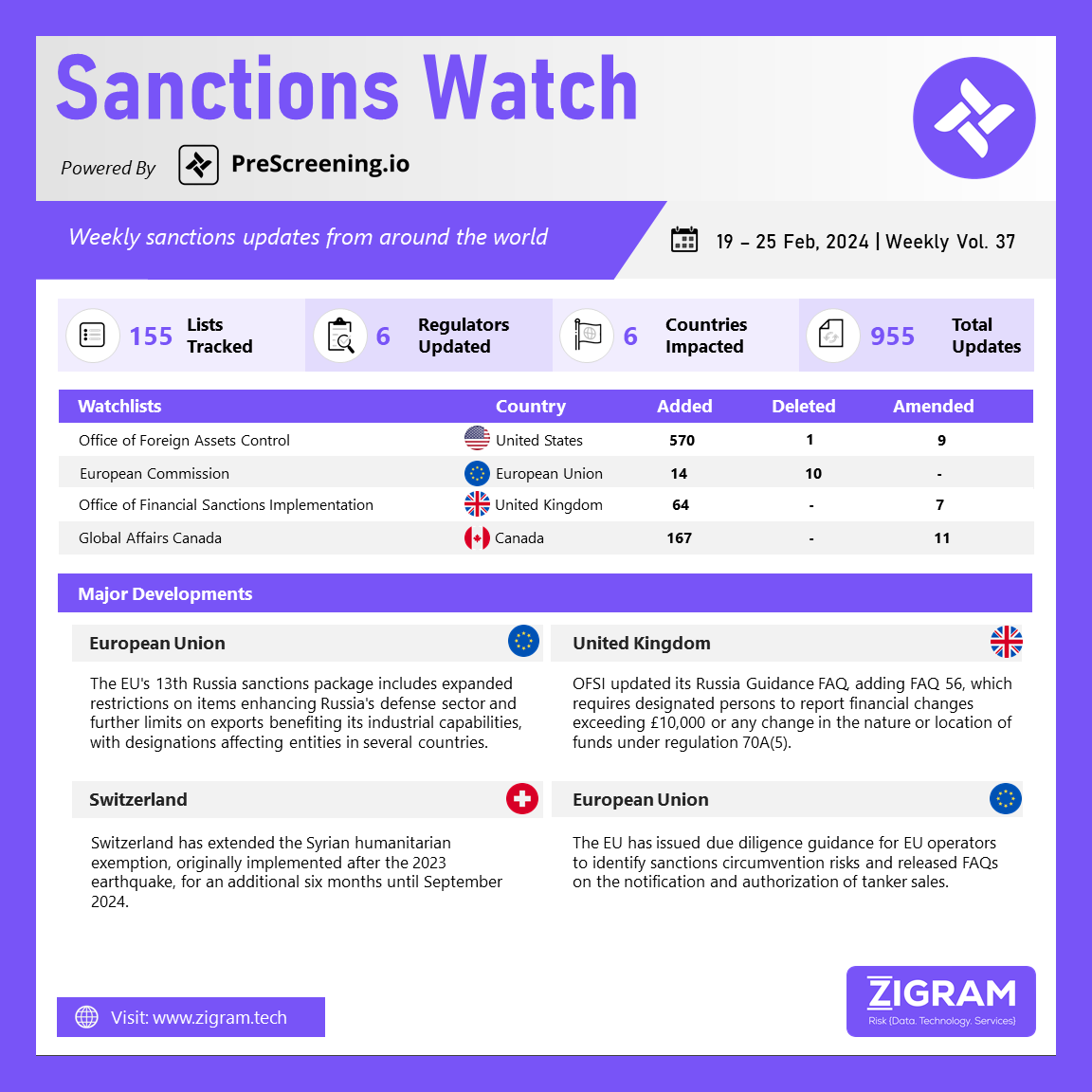
In the latest edition of our Sanctions Watch weekly digest, we present significant updates on sanction watchlists and regulatory developments.
The European Union has implemented its 13th package of sanctions against Russia, which includes an expanded list of restricted items that could potentially enhance Russia’s defense sector technologically. Furthermore, the sanctions introduce additional restrictions on exports of goods that could enhance Russia’s industrial capabilities. The measures include designations and updates such as: imposing enhanced restrictions on dual-use goods for entities located in third countries, including India, Sri Lanka, China, Serbia, Kazakhstan, Thailand, and Türkiye, who have been involved in circumventing trade restrictions; targeting entities and associated individuals in Russia’s military and defense sectors, including those facilitating armament supply to Russia from the DPRK; sanctioning members of the Russian judiciary, local politicians, and others responsible for the deportation and re-education of Ukrainian children; targeting Russian entities involved in electronic component development and supply; imposing restrictions on goods such as electrical transformers, static converters, inductors, and aluminum capacitors that could be used in UAV production and contribute to Russia’s industrial capabilities; adding the UK to the list of partner countries applying import controls on iron and steel from Russia; updating the list of common high-priority items; and providing FAQs on the “no re-export to Russia” clause, offering guidance on the requirement to include such a clause in export contracts for specific types of sensitive goods.
The Office of Financial Sanctions Implementation has introduced FAQ 56 regarding the obligation of designated individuals to inform OFSI about changes in their financial status. Under regulation 70A(5), individuals must promptly report changes in their financial situation to OFSI. This includes reporting when the total value of their funds or economic resources has increased or decreased by more than £10,000 compared to their last report to OFSI. Additionally, individuals must inform OFSI if there has been any change in the nature or location of their funds or economic resources that exceeds £10,000. This requirement applies to both individual changes and changes in multiple funds or economic resources of the same type that exceed £10,000.
On February 21, 2024, the Federal Council of Switzerland extended the temporary humanitarian exemption to the sanctions regime against Syria by six months, now effective until September 12, 2024. This exemption was initially introduced after the 2023 earthquake in Syria, which exacerbated the already dire humanitarian crisis in the country. Following the earthquake, the EU amended its measures against Syria on February 23, 2023, to include a six-month humanitarian exemption for international organizations and specific humanitarian actors. This exemption was extended for an additional six months on December 18, 2023. Switzerland decided on March 10, 2023, to incorporate the EU’s temporary humanitarian exemption into its ordinance on measures against Syria. This exemption allows for certain activities necessary for humanitarian work to be exempt from targeted financial sanctions. Switzerland initially adopted sanctions against Syria on May 18, 2011, aligning with the EU’s measures adopted on May 9, 2011, and has since adjusted its measures to align with the EU’s decisions.
The European Union has issued guidelines for EU operators to recognize and address risks related to sanctions evasion. The guidance includes a strategic risk assessment process involving threat and vulnerability identification, risk analysis, design and implementation of mitigating measures, and regular updates. It also outlines best practices for stakeholders, transactions, and goods, and highlights measures to prevent the diversion of exports to/from Russia, emphasizing enhanced vigilance for correspondent accounts. Additionally, the guidance includes red flags for circumvention, such as indirect transactions and complex trust structures associated with countries friendly to Russia. Furthermore, the EU has released FAQs regarding the notification and authorization of tanker sales, explaining the new requirements for oil tanker vendors, the applicability of these requirements, steps vendors should take to prevent vessel sales for use in Russia, and other pertinent aspects of the new regulations.
- #EU
- #13thPackage
- #Russia
- #Ukraine
- #UAV
- #OfficeofFinancialSanctionsImplementation
- #FederalCouncilofSwitzerland
- #FAQ
- #Regulations
- #EuropeanUnion
- #SanctionsWatch
- #RegulatoryCompliance
- #TradeCompliance
- #SanctionsEnforcement
- #SanctionsMonitoringBoard
- #RegulatoryObligations
- #SanctionsBreaches
- #Compliance
- #FAQ