Published Date:
In the latest edition of our Sanctions Watch weekly digest, we present significant updates on sanction watchlists and regulatory developments.
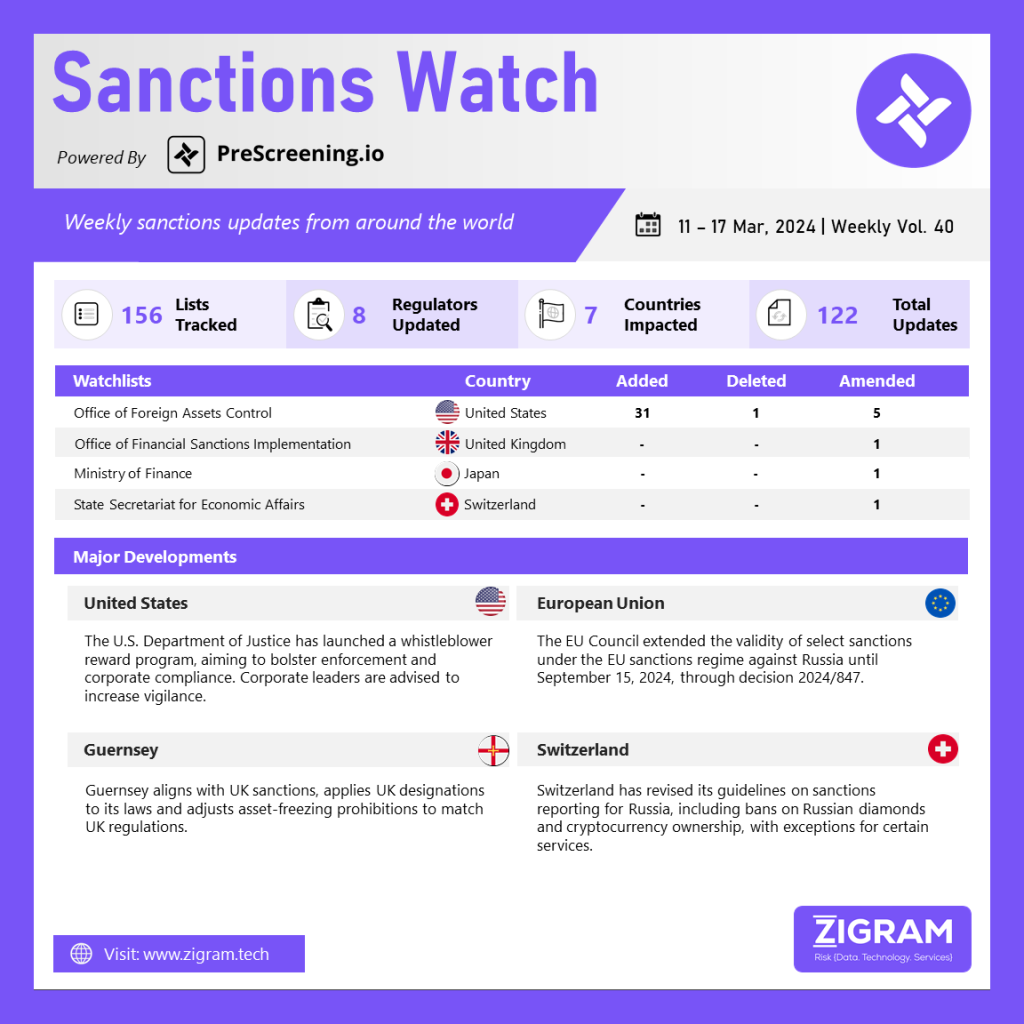
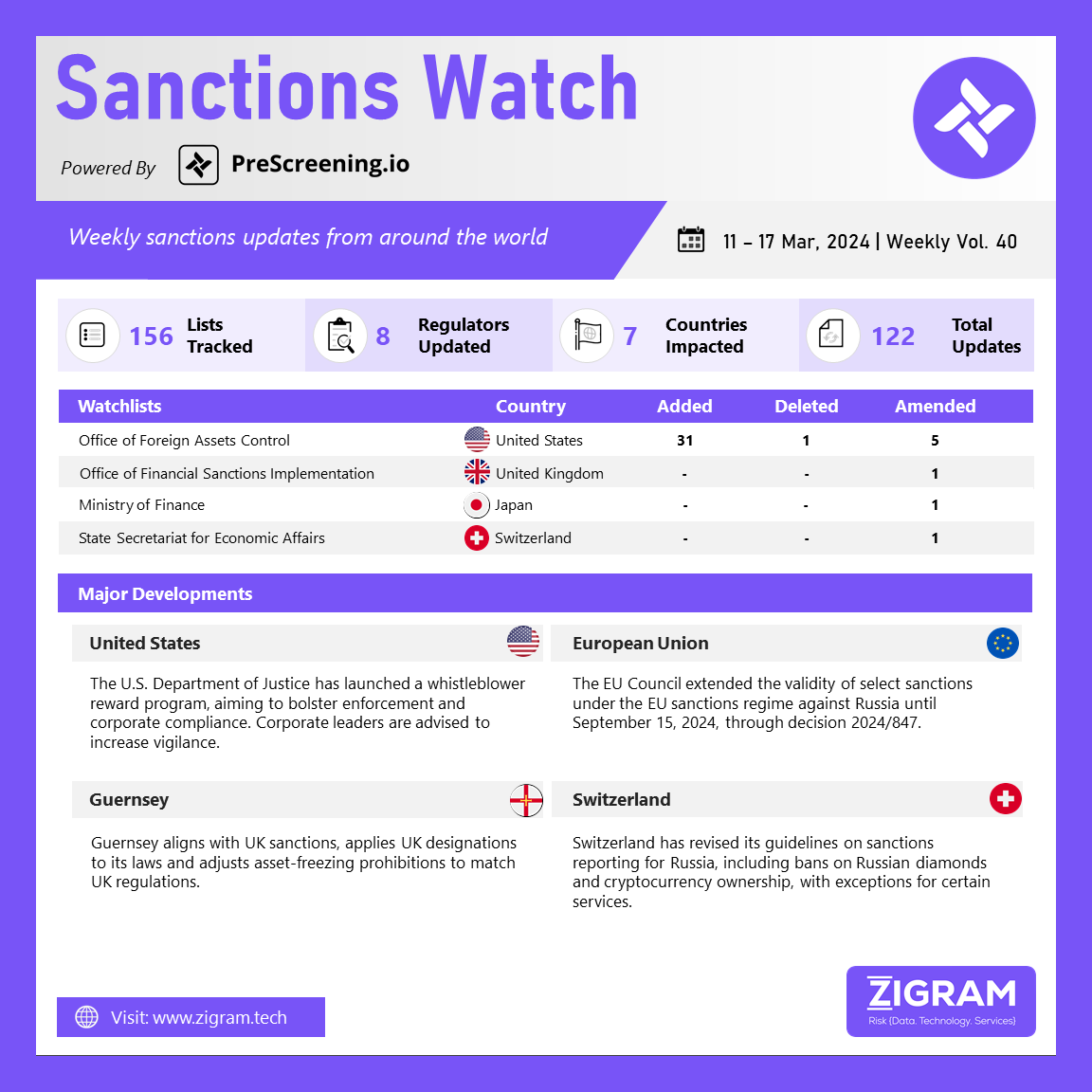
US Deputy Attorney General Lisa Monaco recently announced a new initiative that will offer financial incentives to whistleblowers who report significant corporate misconduct to the Department of Justice (DOJ). This announcement marked the beginning of a 90-day period to develop a pilot program, with the official launch expected later this year. The program aims to address gaps in current enforcement mechanisms, encourage individuals to report misconduct, and prompt companies to enhance their internal reporting and compliance systems. While specific details are still forthcoming, the recent increase in whistleblower activity in other federal programs suggests that corporate leaders and compliance officers should prepare for potentially heightened whistleblower engagement and should thoroughly assess internal whistleblower and employment grievances. This new program, different from existing ones, seeks to systematically expand the DOJ’s use of its authority to target alleged corporate misconduct, offering rewards to whistleblowers whose information leads to significant civil or criminal asset forfeiture.
The EU has decided to extend for an additional six months the sanctions against individuals responsible for threatening Ukraine’s territorial integrity, sovereignty, and independence until September 15, 2024. These measures include travel restrictions, asset freezes, and bans on providing funds or resources to the listed individuals and entities. The sanctions cover over 2100 individuals and entities, many targeted due to Russia’s ongoing military aggression against Ukraine. Three individuals were delisted, and nine deceased persons were removed from the list during the sanctions’ review. Following Russia’s military aggression against Ukraine starting February 24, 2022, the EU significantly expanded sanctions against Russia to weaken its economic base, limit critical technologies and markets, and hinder its ability to wage war. In December 2023, the European Council reiterated its condemnation of Russia’s aggression and expressed unwavering support for Ukraine’s independence, sovereignty, and territorial integrity, emphasizing the need to further weaken Russia’s ability to wage war through sanctions and their effective implementation.
Guernsey has issued the Sanctions (Miscellaneous Amendments) Regulations 2024 and the Terrorist Asset-Freezing (Bailiwick of Guernsey) Law 2011 (Amendment) Regulations 2024. These regulations align the wording of these measures with UK sanctions regimes applicable in Guernsey. They clarify that UK-designated persons are subject to prohibitions as if designated under the Guernsey Terrorist Asset-Freezing Law 2011. Additionally, amendments to the Guernsey Terrorist Asset-Freezing Law 2011 bring its prohibitions in line with UK sanctions regimes.
Switzerland has recently updated its guidelines regarding sanctions reporting requirements related to Russia, focusing on key areas such as the ban on Russian diamonds, cryptocurrency ownership for Russian nationals, and exceptions to prohibitions on specific services. These revisions indicate a nuanced approach by Switzerland in aligning with international sanctions regimes targeting Russia. The ban on Russian diamonds is aimed at curbing financial flows benefiting Russian entities, while the prohibition on cryptocurrency ownership by Russian nationals reflects efforts to restrict alternative financial channels. The exceptions to certain service prohibitions suggest a balanced approach to compliance, ensuring legitimate activities are not unduly affected. Overall, these updates underscore Switzerland’s commitment to enforcing sanctions while managing the impact on legitimate businesses and individuals.
- #UnitedStates
- #Whistleblowers
- #DepartmentofJustice
- #EuropeanUnion
- #Ukraine
- #TravelBan
- #AssetFreeze
- #Guernsey
- #Terrorist
- #DesignatedPersons
- #SanctionsWatch
- #RegulatoryCompliance
- #TradeCompliance
- #SanctionsEnforcement
- #SanctionsMonitoringBoard
- #RegulatoryObligations
- #SanctionsBreaches
- #Compliance
- #Switzerland
- #RussianDiamond