Sanctions Watch 57
In the latest edition of our Sanctions Watch weekly digest, we present significant updates on sanction watchlists and regulatory developments.
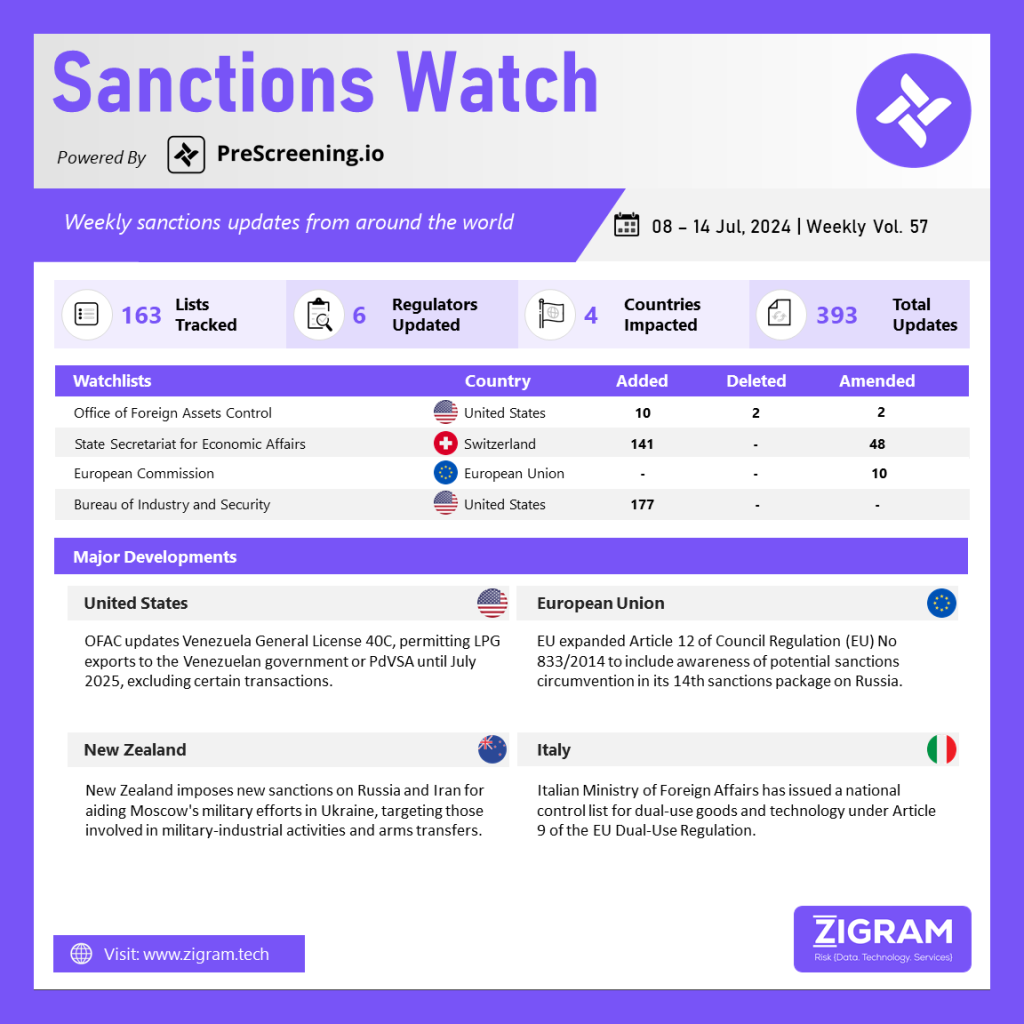
The Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) has updated Venezuela General License 40C, authorizing transactions related to the exportation or reexportation of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) to Venezuela until July 8, 2025. This includes dealings with the Government of Venezuela, Petróleos de Venezuela, S.A. (PdVSA) and entities with a 50% or greater interest held by PdVSA. This authorization aligns with Executive Orders 13850, 13857 and 13884, under the Venezuela Sanctions Regulations, 31 CFR part 591. However, it does not permit payment-in-kind of petroleum products or transactions otherwise prohibited by the regulations.
This includes dealings with blocked persons other than PdVSA or entities significantly owned by it and Government of Venezuela persons blocked solely under E.O. 13884. Effective July 8, 2024, General License 40B will be replaced by 40C. Compliance with other Federal agencies, like the Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security, is still required.
As part of the 14th package of EU sanctions on Russia, the EU has expanded the definition of sanctions circumvention under Article 12 of Council Regulation (EU) No 833/2014. The original provision prohibited knowingly and intentionally engaging in activities aimed at circumventing the sanctions. The amended Article 12 now extends this prohibition to include participation in activities that could potentially lead to circumvention, even if the participant does not deliberately seek that outcome but is aware that their involvement might have that effect and accepts the possibility. This expansion aims to close loopholes and enhance the effectiveness of sanctions by holding individuals and entities accountable for indirect involvement in sanctions evasion, thereby strengthening the EU’s regulatory framework against sanctions circumvention.
New Zealand has expanded its sanctions against Russia and Iran in response to their involvement in the Ukraine conflict. Foreign Minister Winston Peters announced that the new sanctions specifically target Russian figures linked to the military-industrial sector and those aiding Russia militarily. This includes designations aimed at individuals and entities facilitating the illicit transfer of weapons from North Korea to Russia for use in Ukraine.
Additionally, the sanctions address Iranian entities supporting Russia through the supply of drones. Peters emphasized New Zealand’s condemnation of any military assistance to Russia, viewing such actions as a threat to Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity. Since February 2022, New Zealand has implemented sanctions on over 1,700 individuals and entities related to the conflict, alongside various trade measures.
The Italian Ministry of Foreign Affairs has released a national control list for dual-use goods and technology, restricted under Article 9 of the EU Dual-Use Regulation. This regulation allows member states to require authorization for exporting dual-use items not listed in Annex I for reasons such as public security, preventing terrorism and human rights considerations. The controlled items include those related to materials processing, electronics and computers.
Know more about the product: PreScreening.io
Click here to book a free demo.
- #OFAC
- #Venezuela
- #GeneralLicense
- #LiquefiedPetroleumGas
- #ExecutiveOrders
- #BlockedPersons
- #BureauofIndustryandSecurity
- #EU
- #SanctionsEvasion
- #UnitedKingdom
- #UK
- #NewZealand
- #Ukraine
- #SanctionsEnforcement
- #SanctionsMonitoringBoard
- #SanctionsRegimes
- #War
- #MilitarySupport
- #NorthKorea
- #Russia
- #TradeMeasures
- #Italy
- #Regulations