- 7 minutes read
FATF Grey List June 2024: Comprehensive Guide On Risks, Criteria, And Compliance Measures
On June 28, 2024, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) released its “Grey List”. FATF identifies jurisdictions that require enhanced scrutiny due to strategic deficiencies in their anti-money laundering and counter-financing of terrorism (AML/CFT) regimes. These jurisdictions, placed under increased monitoring, undergo rigorous evaluations aimed at addressing vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance with international standards. This scrutiny not only safeguards the integrity of the international financial system but also fosters cooperation among nations in combating illicit financial activities. This introduction explores the implications and measures associated with jurisdictions on the FATF’s increased monitoring list, highlighting efforts to strengthen global financial security and regulatory frameworks.

When the FATF places a jurisdiction under increased monitoring, it means the country has committed to resolve swiftly the identified strategic deficiencies within agreed timeframes and is subject to increased monitoring. This list is often externally referred to as the grey list.

The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1989 on the initiative of the G7 to develop policies to combat money laundering. In 2001, its mandate was expanded to include efforts to combat terrorism financing. The FATF sets international standards aimed at preventing these illegal activities and the harm they cause to society. With 39 members including major economies and regional organizations, the FATF works collaboratively to promote the effective implementation of legal, regulatory, and operational measures for combating money laundering, terrorist financing, and other related threats to the integrity of the international financial system.
FATF Key Takeaways
- The FATF plays a crucial role in combating global money laundering and terrorist financing by setting international standards and monitoring compliance.
- The Grey List and Black List are tools used by the FATF to identify countries with deficiencies in their AML/CTF regimes and to encourage them to make necessary reforms.
- Being grey-listed or black-listed can have severe economic and reputational consequences for a country.
- Countries must implement comprehensive legal, regulatory, and institutional measures to address AML/CTF deficiencies and to avoid being grey-listed or black-listed.
- Continuous monitoring, international cooperation, and proactive engagement with both public and private sectors are essential for maintaining compliance with FATF standards and safeguarding the integrity of the global financial system.
FATF Grey List And Black List

What Are The Reasons For Grey Listing Of A Country?
- A country has significant gaps in its AML/CTF framework.
- A country lacks adequate regulatory measures to monitor and control money laundering and terrorist financing.
- A country fails to demonstrate sufficient progress in implementing FATF recommendations during evaluations.
Newly Added Jurisdictions Under Increased Monitoring – June 2024
Monaco 
Monaco will further its action plan by understanding risks related to money laundering and tax fraud abroad, increasing efforts to seize criminal assets internationally, enhancing sanctions for AML/CFT breaches, completing FIU resourcing, improving judicial efficiency, and increasing the seizure of criminally derived property.
Venezuela 
Venezuela will work to implement its action plan by: deepening its understanding of ML/TF risks; ensuring comprehensive AML/CFT measures and risk-based supervision for all financial entities; maintaining accurate beneficial ownership information; bolstering FIU resources and financial intelligence use; improving ML and TF investigation and prosecution; preventing NPO abuse for TF while protecting legitimate activities; and promptly applying TF and PF-related financial sanctions.
Jurisdictions Under Increased Monitoring – June 2024 (Grey List)
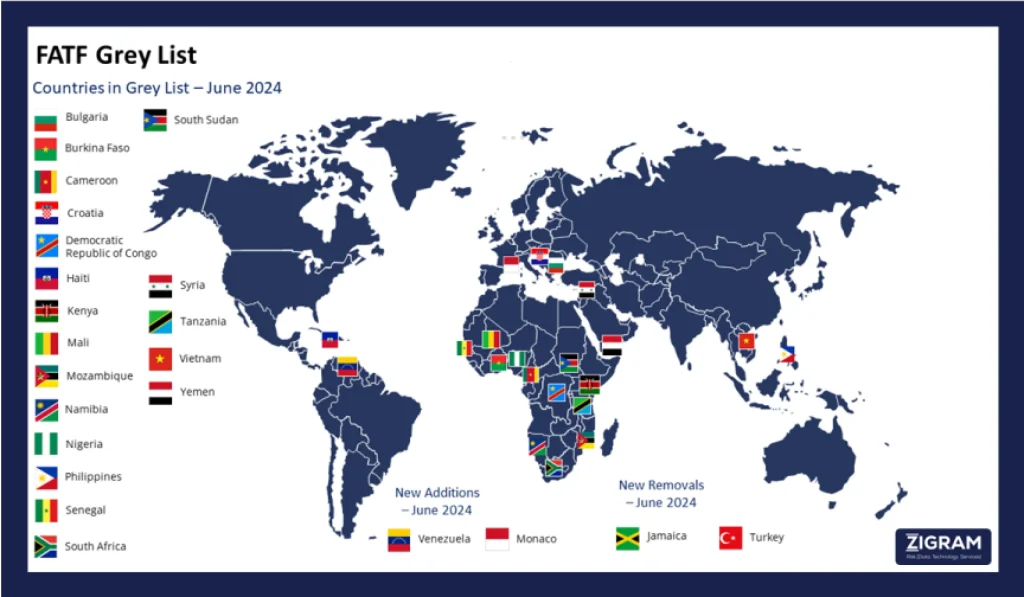
The FATF allows jurisdictions without immediate deadlines to voluntarily report their progress. Since February 2024, the FATF has reviewed progress from Bulgaria, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Croatia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Haiti, Jamaica, Mali, Mozambique, Nigeria, the Philippines, Senegal, South Africa, South Sudan, Tanzania, Turkey, and Vietnam, with updated statements provided below. Kenya, Namibia, Syria, and Yemen chose to defer reporting, so their previous statements are included and may not reflect their current AML/CFT status. After the review, the FATF now also identifies Monaco and Venezuela.
What Measures Can Countries Take to Be Removed from the Grey List?
- Enhance Legal Framework: Implement robust laws and regulations to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Strengthen Institutional Capacity: Establish competent authorities and provide them with adequate resources and training to enforce AML/CTF measures.
- Improve Transparency: Ensure transparency in financial transactions and beneficial ownership information.
- International Cooperation: Enhance cooperation with international bodies and other countries to combat cross-border financial crimes.
- Regular Reporting: Submit regular progress reports to FATF and undergo follow-up evaluations to demonstrate ongoing compliance.
Jurisdictions No Longer Subject To Increased Monitoring By The FATF
Jamaica 
“Jamaica is no longer under the FATF’s increased monitoring process but should continue working with CFATF to maintain its AML/CFT improvements”
Jamaica enhanced its AML/CFT system to address the FATF's 2020 concerns by:
- Gaining a better understanding of its ML/TF risks.
- Including all financial institutions and DNFBPs in the AML/CFT regime with risk-based supervision.
- Preventing misuse of legal entities for criminal purposes and ensuring accurate beneficial ownership information.
- Increasing ML investigations and prosecutions, and using financial intelligence effectively.
- Implementing prompt financial sanctions for terrorist financing.
- Applying a risk-based approach to supervising its NPO sector to prevent TF abuse.
Turkey 
“Turkey is no longer under FATF’s increased monitoring but should continue collaborating with the FATF to sustain its AML/CFT improvements, especially in NPO sector oversight”
Turkey significantly improved its AML/CFT regime to address deficiencies identified in October 2021 by:
- Increasing FIU resources for supervising high-risk sectors and conducting more on-site inspections.
- Imposing strong sanctions for AML/CFT breaches, especially for unregistered money services and exchange offices.
- Enhancing financial intelligence usage to support ML investigations and proactive FIU dissemination.
- Conducting more complex ML investigations and prosecutions.
- Defining clear responsibilities and objectives for authorities handling asset recovery and TF cases, using data for risk assessments and policy updates.
- Prioritizing TF investigations and prosecutions, particularly related to UN-designated groups, and extending investigations to identify support networks.
- Pursuing financial sanctions under UNSCRs 1373 and 1267, and making domestic designations in line with risk profiles.
- Implementing a risk-based oversight approach for NPOs, engaging with them, ensuring proportional sanctions, and avoiding disruption of legitimate activities.
How Can Countries Avoid Being Added To The Grey List?
1-Implementing Robust AML/CTF Framework
Countries need to develop and enforce comprehensive anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) laws and regulations and ensure that these frameworks are aligned with FATF recommendations and are capable of effectively addressing identified risks.
2-Continuous Risk Assessment And Mitigation
Regularly assessing the national risks of money laundering and terrorist financing is important. Countries should update policies and procedures based on these assessments to mitigate emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
3-Strengthening Institutional Capacity
Investing in building the capacity of financial intelligence units (FIUs), law enforcement agencies, and other relevant authorities is a key factor. Regulatory bodies need to provide adequate resources, training, and tools to these institutions to ensure effective enforcement of AML/CTF measures.
4-Enhancing Transparency And Accountability
Countries should ensure transparency in financial transactions and beneficial ownership information and implement measures to prevent the misuse of corporate structures and other legal entities for money laundering and terrorist financing.
5-Fostering International Cooperation And Coordination
Engaging actively in international cooperation and information sharing with other countries and relevant international organizations is necessary. Countries must participate in FATF peer reviews and mutual evaluations, and promptly address any identified deficiencies and collaborate with both the public and private sectors to create a unified approach in combating financial crimes.
The June 2024 update on FATF jurisdictions under increased monitoring reflects ongoing global efforts to combat money laundering, terrorist financing, and proliferation financing. The progress and challenges highlighted for each jurisdiction demonstrate the complexity and variability of implementing effective Anti-Money Laundering (AML) / Counter Terror Financing (CFT) measures. Continuous monitoring and assistance from FATF and its regional bodies are crucial to ensure that these jurisdictions address their strategic deficiencies effectively. The commitment of these countries to enhance their financial systems and regulatory frameworks is essential for maintaining global financial integrity and security. Going forward, it remains imperative for international cooperation and compliance to stay robust, ensuring a cohesive and comprehensive response to financial crimes worldwide.
ZIGRAM is the key to enhancing compliance. By leveraging technology to streamline and automate regulatory processes through advanced data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, ZIGRAM helps by leveraging technology to streamlining and automating regulatory processes through advanced data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. By providing customized scalable solutions tailored to specific regulatory challenges, ZIGRAM helps financial institutions to stay ahead of evolving compliance standards, reduce operational costs, and enhance overall transparency and trust in the financial system.
- #FATF
- #GreyList
- #AMLCFT
- #Compliance






