Published Date:
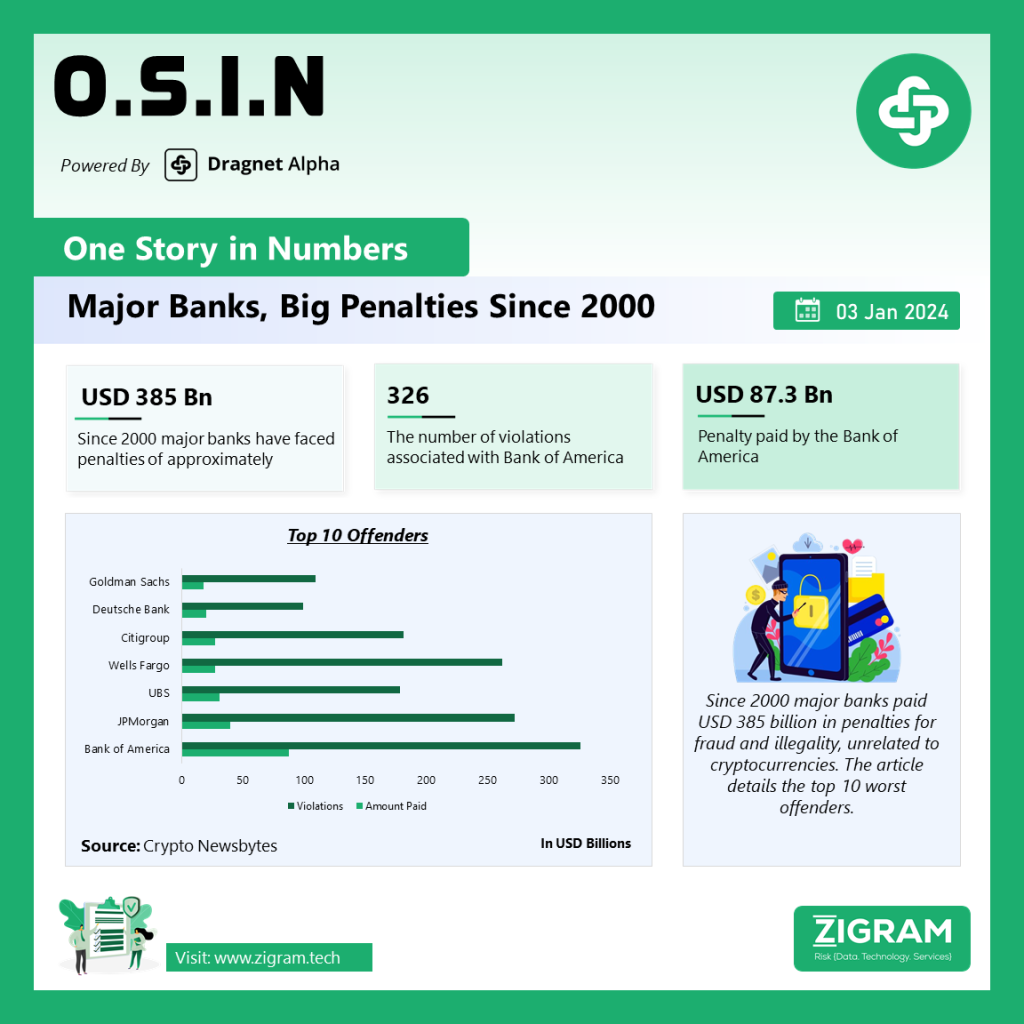
The article discusses the substantial penalties imposed on major banks for fraudulent activities and illegality, totaling a staggering USD 385 billion since the year 2000. It is important to note that these penalties are not related to cryptocurrencies, highlighting issues within the traditional financial sector.
The top 10 worst offenders in this regard are outlined in the article, shedding light on the extent of misconduct within established financial institutions. These penalties arise from a variety of infractions, including market manipulation, money laundering, and violations of regulatory standards.
The piece emphasizes that the significant penalties these banks face underscore the importance of addressing ethical concerns and ensuring accountability in the financial industry. The scale of these fines raises questions about the efficacy of existing regulatory frameworks and the need for stronger measures to deter unlawful practices.
One of the key points made in the article is that despite the astronomical fines, some critics argue that these penalties may not be sufficient to deter banks from engaging in illicit activities. The recurring nature of such penalties for certain institutions suggests that there may be systemic issues within the banking sector that need to be addressed.
Additionally, the article explores the impact of these penalties on the reputation and public trust in the banking industry. The repeated instances of misconduct have eroded the credibility of major banks, leading to increased skepticism among the general public. Rebuilding trust becomes crucial for these financial institutions to maintain their standing in the market.
While the focus is on the penalties imposed on traditional banks, the article also indirectly highlights the ongoing debate around the role of cryptocurrencies in illicit activities. By emphasizing that the discussed penalties are unrelated to cryptocurrencies, it aims to dispel misconceptions and underscore that fraudulent activities exist across various financial sectors.
In conclusion, the article serves as a comprehensive overview of the substantial penalties levied against major banks for fraud and illegality since 2000. It not only provides a list of the top 10 worst offenders but also raises critical questions about the effectiveness of current regulatory measures and the need for a more robust system to prevent future misconduct. Ultimately, the financial industry must address these issues to rebuild trust and ensure the integrity of the global financial system.
- #BankingPenalties
- #FinancialMisconduct
- #RegulatoryFramework
- #EthicalFinance
- #BankingScandals
- #TrustInBanking
- #MarketManipulation
- #MoneyLaundering
- #FinancialIntegrity
- #Top10Offenders
- #CorporateAccountability
- #RegulatoryChallenges
- #GlobalFinance
- #PenaltiesInBanking
- #PublicTrustIssues
- #BankReputation