Published Date:
In the latest edition of our Sanctions Watch weekly digest, we present significant updates on sanction watchlists and regulatory developments.
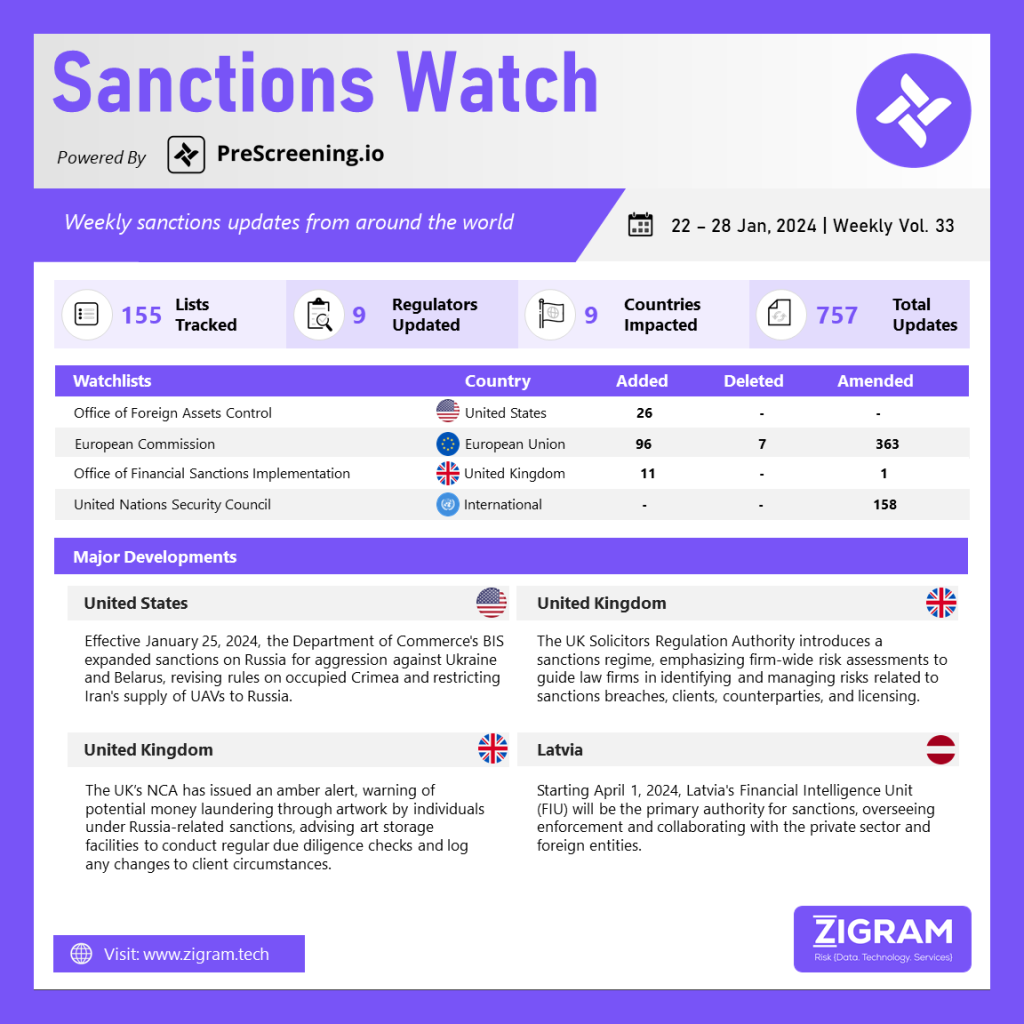
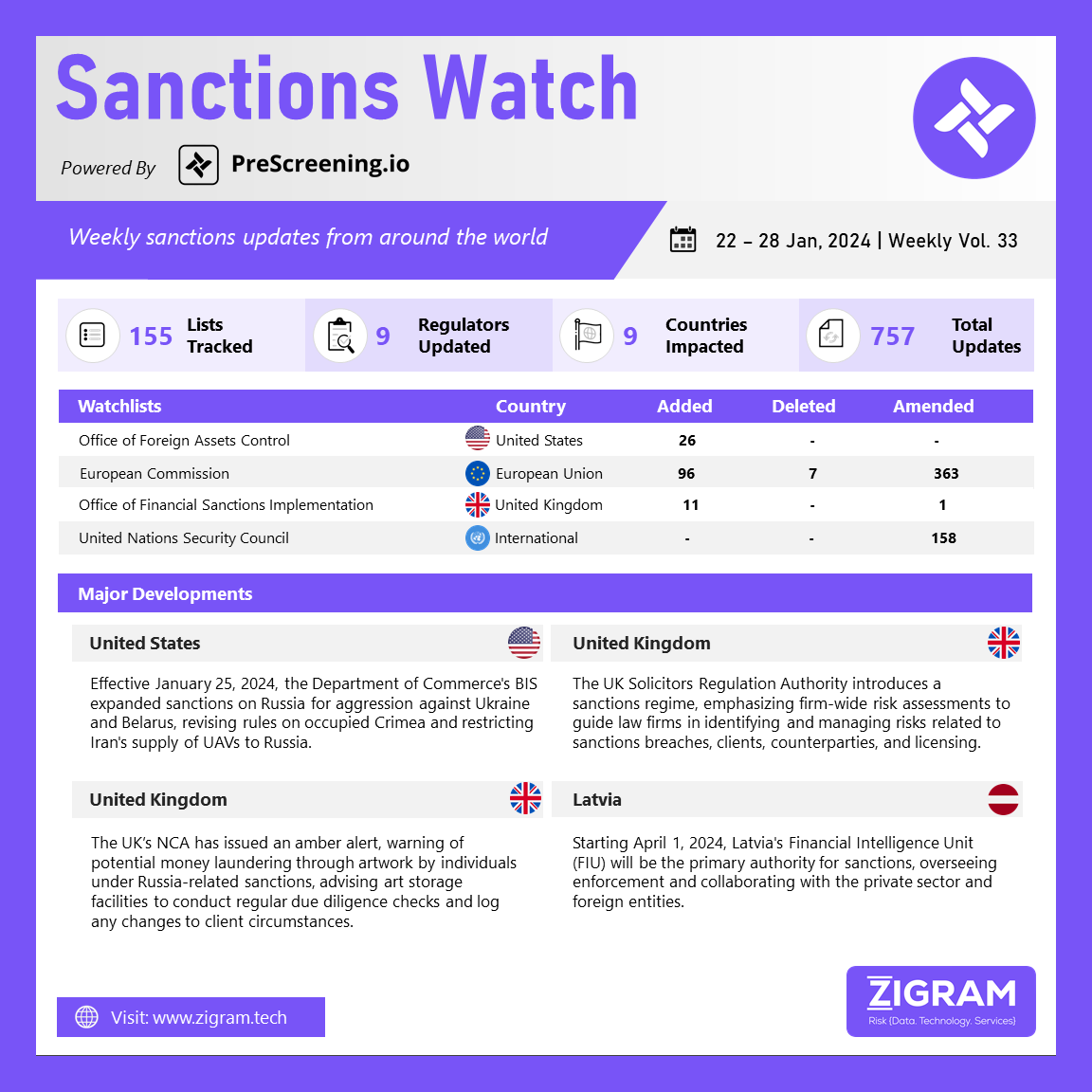
On January 25, 2024, the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) within the Department of Commerce strengthened controls under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) regarding Russia and Belarus. The update involves expanding the list of restricted products for export to these countries by introducing 95 new Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) codes. This extension includes various items such as chemicals, lubricants, metals, and Chapter 88 of the HTS, affecting Russia’s access to inputs for its defense industry. Additionally, BIS imposed tighter controls on Russia’s acquisition of unmanned aerial vehicles from Iran. Notably, the changes eliminate de minimis treatment for specific military and spacecraft-related items, broadening the scope of EAR and making it more challenging for foreign suppliers to provide certain items to Russia and Belarus. The adjustments also include clarifications and harmonizing changes, including an exclusion from BIS license requirements for transactions related to deployments by the Armed Forces of Ukraine in the temporarily occupied Crimea region and covered regions of Ukraine.
The United Kingdom Solicitors Regulation Authority has introduced a sanctions regime, emphasizing firm-wide risk assessments as a crucial tool for guiding law firms in navigating legal and regulatory obligations. The published guidance comprehensively addresses the identification of individuals at risk of being implicated in sanctions breaches and evaluates the potential risks posed by clients and counterparties. Emphasizing the significance of implementing firm-wide risk assessments, the guidelines outline the key elements of an effective sanctions risk assessment. The distinction between matter-specific and firm-wide risk assessments is clarified, shedding light on their respective roles. Additionally, the guidance provides valuable insights into licensing matters, contributing to a holistic understanding of the regulatory landscape. This initiative aims to enhance compliance within law firms by offering a detailed framework for assessing and mitigating sanctions-related risks, ensuring a comprehensive approach to regulatory adherence.
The United Kingdom’s National Crime Agency (NCA) has issued an amber alert, cautioning artwork storage facilities about potential money laundering by individuals under Russia-related sanctions. Responsible for enforcing sanctions after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the NCA focuses on high-net-worth individuals, like Russian oligarchs, who often store art for investment or tax purposes. Emphasizing regular due diligence checks, the agency aims to curb criminals and sanctioned individuals evading financial sanctions through art services. Adrian Searle, Director of the National Economic Crime Centre at the NCA, underscores the art market’s attractiveness to money launderers and calls for increased vigilance from the sector, positioning it as a vital gatekeeper. The NCA reveals instances, including a Hezbollah member handling £1m worth of fine art in UK storage and an organized crime group exploiting a shipping company for ‘cultural properties,’ either fake or illicitly removed, demonstrating the need for heightened scrutiny in combating illicit financial activities in the art market.
Starting April 1, 2024, the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) is set to transition into Latvia’s primary competent authority for sanctions. Currently focused on combating sanctions evasion, the FIU will broaden its role post the aforementioned date. Its expanded responsibilities will include not only enforcement but also the provision of guidance, and facilitation of communication with the private sector and foreign institutions. This transition signifies a comprehensive shift, as the FIU evolves from solely countering sanctions evasion to a central entity overseeing and implementing various facets of sanctions-related activities. By assuming a more extensive role, the FIU aims to enhance its effectiveness in addressing financial irregularities and promoting cooperation between public and private entities within and internationally.
- #BIS
- #UnitedStates
- #DepartmentofCommerce
- #Russia
- #Belarus
- #UnmannedAerialVehicles
- #Iran
- #Ukraine
- #UnitedKingdom
- #SolicitorsRegulationAuthority
- #SanctionsWatch
- #RegulatoryCompliance
- #TradeCompliance
- #SanctionsEnforcement
- #SanctionsMonitoringBoard
- #RegulatoryObligations
- #SanctionsBreaches
- #Compliance
- #RegulatoryAdherence
- #NationalCrimeAgency
- #Alert
- #MoneyLaundering
- #FinancialIntelligenceUnit
- #Latvia
- #FinancialIrregularities